Continuing Education

Continuing Education
Continuing professional development (CPD) involves not only educational activities to enhance medical competence in medical knowledge and skills, but also in management, team building, professionalism, interpersonal communication, technology, teaching, and accountability.
CME's concept generally refers to expanding medical knowledge, skills, and attitudes, also incorporates and exceeds this concept by acknowledging a wide range of competencies needed to practice high-quality medicine, including medical, managerial, ethical, social, and personal skills. CPD integrates every physician's ethical responsibility and increases job satisfaction. A continuing process, outside formal undergraduate and postgraduate training, allows individual doctors to maintain and improve standards of medical practice through the development of knowledge, skills, attitudes, and behavior. CPD should also support specific changes in practice.
The wide-ranging competencies beyond the clinical update, research and scientific writing, multidisciplinary context of patient care, ethical practice, communication, management and behavioral skills, team building, information technology, audit, and appropriate attitudinal change to ensure improved patient outcomes and satisfaction.
Medical Assistant

Medical Assistant (MA) is not a licensed profession. An MA is a professionally multi-skilled person who assists in limited aspects of medical practice under the direct supervision and responsibility of a physician. These limited tasks include patient care management, administrative and clinical procedures, and managerial and supervisory functions. Competence in the field also requires that a medical assistant adhere to ethical and legal standards of professional practice, recognize and respond to emergencies, and demonstrate professional characteristics. They work under the direct supervision and responsibility of a licensed physician.
- Performing Clinical Procedures, to include:
- Performing Aseptic Procedures.
- Taking Vital Signs.
- Preparing Patients For The Physician's care.
- Performing Venipuncture And Non-intravenous injections.
- Observing And Reporting Patients' signs or symptoms.
- Administering basic first aid.
- Assisting with patient examination or treatments.
- Operating office medical equipment.
- Collecting routine laboratory specimens as directed by the physician.
- Administering medication as directed by the physician.
- Performing basic laboratory procedures.
- Performing office procedures, including all general administrative duties required by the physician.
- Performing dialysis procedures, including home dialysis.
MAs may not prescribe legend or controlled substances.
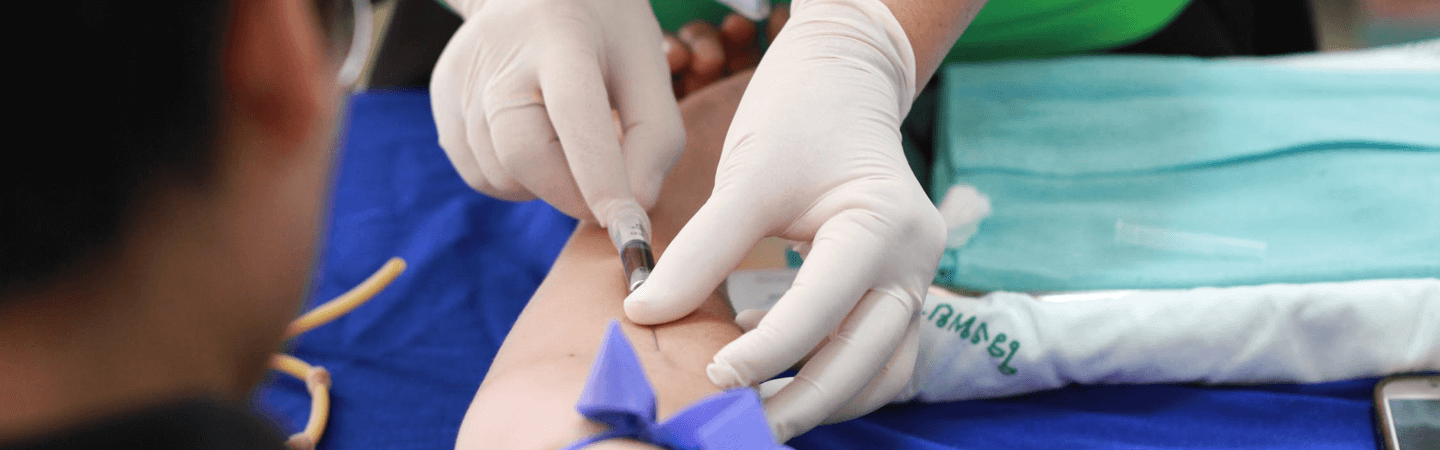
Phlebotomy Technician
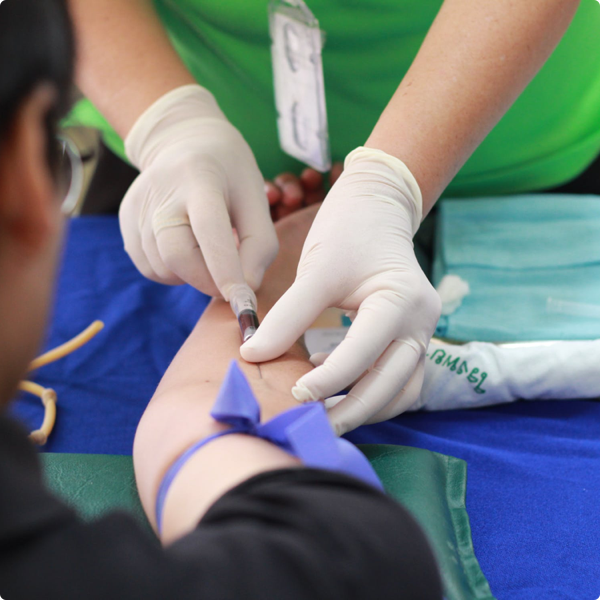
Phlebotomists are professionals who draw blood from patients. They take these blood samples, pass them to the laboratory and check for health issues, like diseases, bacteria, cholesterol, etc. In the meantime, phlebotomists can work in all kinds of medical facilities, from hospitals to private laboratories.
- Drawing blood from patients and blood donors
- Evaluating patients' ability to withstand the procedure and helping them feel comfortable
- Explaining the blood-drawing procedure to patients and answering questions
- Performing basic point-of-care testing, such as reading blood glucose levels
- Preparing blood, urine, and other specimens for testing
- Maintaining medical equipment such as needles, test tubes, and blood vials
Electrocardiograph Technician (EKG)
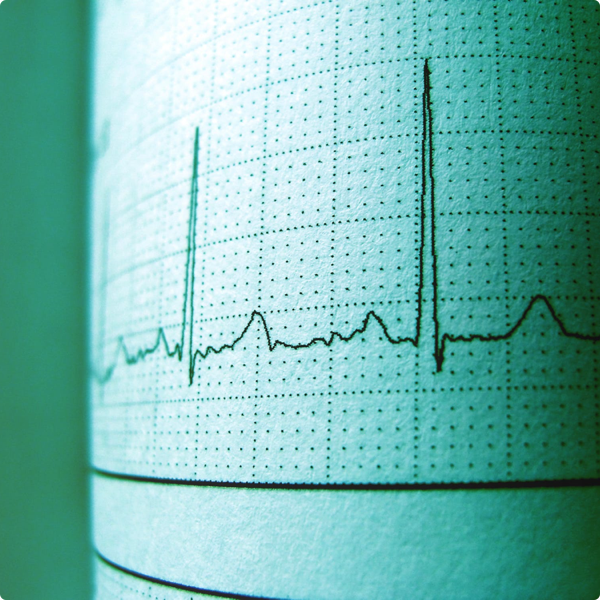
EKG technicians are part of the allied health sector and typically provide direct patient care in hospitals or clinics. KG techs are also a fundamental part of any cardiology department. Using specialized equipment (like EKG machines) to measure the heart’s efficiency, EKG techs help with routine physical exams and screening procedures before surgeries.
EKG techs will also need to comfort patients, as well as record and provide information to the overseeing physician. Precise and accurate diagnostic images are crucial so physicians can make accurate diagnoses. Some of your patients will be anxious or in pain, so that you will need good communication and compassion skills. Staying in good physical shape is also crucial, as you may be expected to spend a lot of time on your feet.
Depending on the job description or the training program, some of the most common titles for this position are:
- Cardiac Monitor Technician
- ECG Technician
- Cardiac Monitor Technician
- Cardiographic Technician
- Rhythm Analysis Technician
- Telemetry Monitor Technician
Telemetry Technician

Telemetry Technicians are also called monitoring technicians or electrocardiograph technicians. They’re trained to recognize heart rhythms.
Telemetry is defined as an electronic system designed to monitor patient heart activity. The heart itself is an electrical system, and cardiac monitors pick up a patient’s heart activity which displays electrical patterns on a computer screen for medical technicians to review.
Telemetry Technicians assist nursing departments by monitoring patient cardiac rhythms. You must demonstrate proficient skills in order to identify patient arrhythmias, abnormalities, or significant cardiac baseline changes. Unusual heart rhythms indicate cardiac trouble or may indicate diseases of the heart which require unique treatments.
Technicians are active in department activities, transdisciplinary team activities, and other activities to ensure individualized, patient-centered health care for all patient populations. Your primary patient is typically your senior adult, 65 years and older. However, with an uptick in younger cardiac patients, your patient demographics can vary.
Telemetry Technicians work alongside Nurses to inform and notify Charge Nurses of any foreseen risk factors in the patients. Your position ensures that medical standards, policies, and procedures are met and maintained to the highest standards. To say that you have an essential role is quite an understatement.
Telemetry Job Duties Include:
- Monitoring a patient's cardiac function.
- Identify significant changes.
- Reading rhythm strips and understanding the data that is reflected.
- Reporting directly to a nurse or healthcare provider.
- Troubleshooting issues with the cardiac monitor.
Patient Care Technician (PCT)

Patient care technicians often referred to as certified nursing assistants, are skillfully trained professionals who provide adequate care to patients in hospitals, medical offices, and nursing homes.
As a patient care technician, they usually always work under the direct supervision of a nurse (RN or LPN) or a doctor, informing them of any problems you may encounter or suspect with your patients.
- Work with the patients, making the visit as comfortable as possible.
- Taking vital signs and taking samples as directed.
- Be willing to help patients with bathroom use, meal service, changing bedding, and other hygiene needs.
- Patient care technicians should also ensure that their patients take detailed notes and perform assessments of their condition.
- Ability to listen, understand and process a variety of detailed information